Extending context window of LLMs#
Note
We present Position Interpolation and YaRN that extends the context window sizes of
RoPE[SLP+23]-based pretrained LLMs such as LLaMA.
Position interpolation#
Large language models (LLMs) typically come with a pre-defined context window size. For example, inputs to LLaMA models must be fewer than 2048 tokens. This pre-set context window limit is frequently exceeded in application. However, training an LLM from scratch with long context windows requires significant investments. This naturally leads to a question: Can we extend the context window of an existing pre-trained LLM?
One straightforward approach is to fine-tune an existing pre-trained Transformer with a longer context window. However, empirically, we found that models trained this way adapt to long context windows very slowly. Position Interpolation, instead of extrapolation, directly down-scale the position indices so that the maximum position index matches the previous context window limit in the pre-training stage.
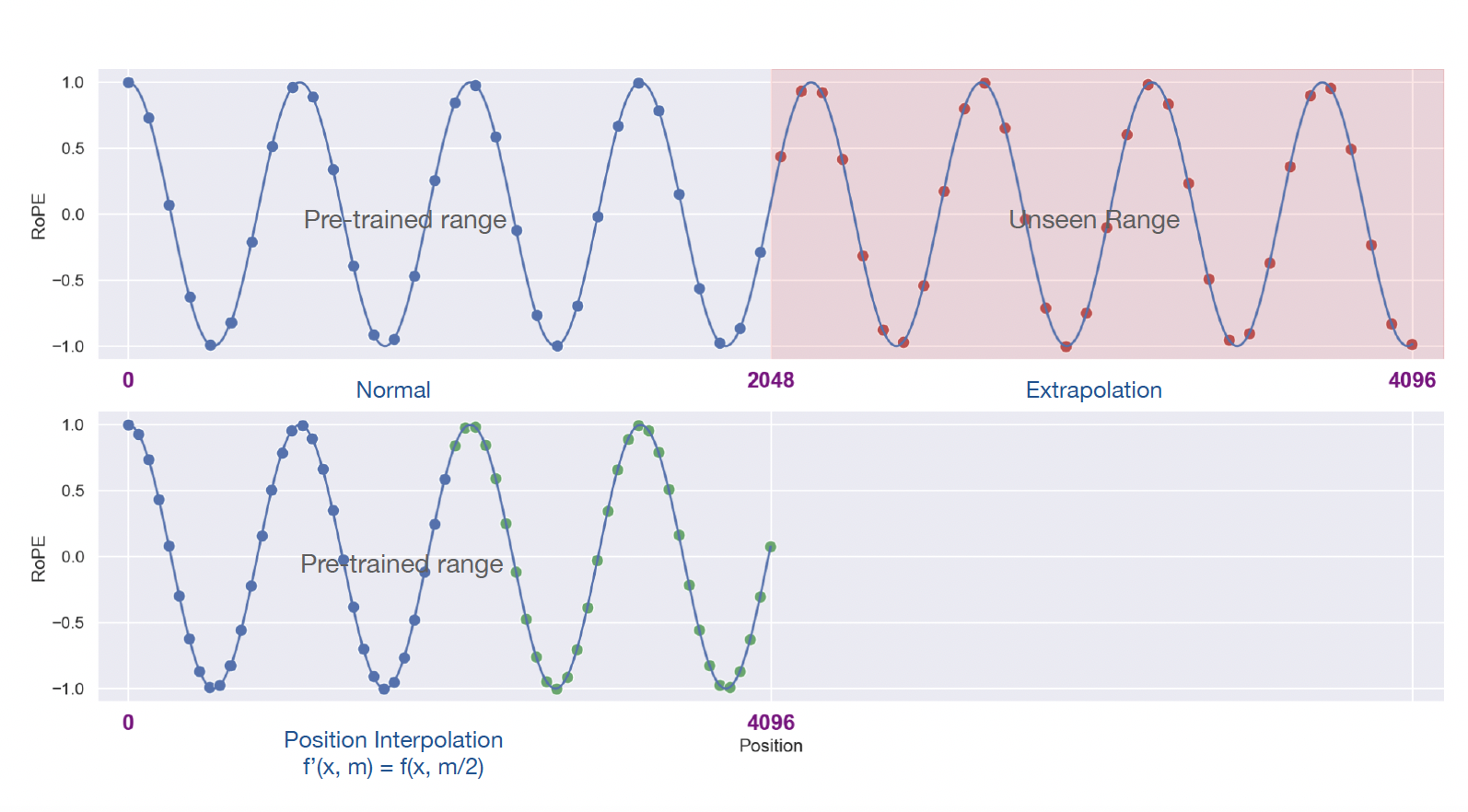
Tip
低维(\(i\to 0\))部分频率高(\(\theta_{i}\to 1\))
高维(\(i\to d/2-1\))部分频率低(\(\theta_{i}\to 1/10000\))
在低维度上旋转角度较大,意味着这些维度上的信号变化非常迅速,能够精细地区分相邻位置。如果在低维度进行内插,对用低维区分不同位置间的能力影响更大,这种现象称之为高频信息的损失。因此我们可采用高频外推,低频内插的方式。
YaRN#
The ratio between the extended context length and the original context length is denoted as \(s = \frac{L'}{L}\). General form of extending context length:
For Position Interpolation, we have \(g(m) = m/s, h(\theta_d) = \theta_d\).
“NTK-aware” interpolation#
Instead of scaling every dimension of RoPE equally by a factor \(s=\frac{L'}{L}\), we spread out the interpolation pressure across multiple dimensions by scaling high frequencies less and low frequencies more.
Definition 1 The “NTK-aware” interpolation is a modification of RoPE with the following functions.
where
Tip
For small \(d\):
thus extrapolation.
To let \((L', b')\) equals to \((L, b)\) on the lowest frequency (\(d=\frac{|D|}{2}-1\)), thus interpolation, we need
this leads to \(b' = b\cdot s^{\frac{|D|}{|D|-2}}\).
“NTK-by-parts” interpolation#
Tip
We choose not to interpolate the higher frequency dimensions at all while always interpolating the lower frequency dimensions. It can be defined with the help of a ramp function.
YaRN#
In addition to the previous interpolation techniques, we also observe that introducing a temperature \(t\) on the logits before the attention softmax has a uniform impact on perplexity, that is
We can use a “length scaling” trick which scales both \(\mathbf{q}_{m}\) and \(\mathbf{k}_{n}\) by a constant factor \(\sqrt{{1}/{t}}\) by simply scaling the complex RoPE embeddings by the same amount. For LLama and LLama 2 models, we recommend the following values: \(\sqrt\frac{1}{t} = 0.1\ln(s) + 1\).
Definition 3 By the “YaRN method”, we refer to a combination of the attention scaling and the “NTK-by-parts” interpolation.
Tip
RoPE 的远程衰减. 计算 \(a(m,n)\) 时:
\(m\) 和 \(n\) 越近,\(\mathbf{R}_{n-m}\) 旋转得越少,高频维度少低频维度多。
\(m\) 和 \(n\) 越远,\(\mathbf{R}_{n-m}\) 旋转得越多,有很多高频维度转了很多圈,随机性很大,一部分正负抵消一部分振荡。
