OpenCoder#
Note
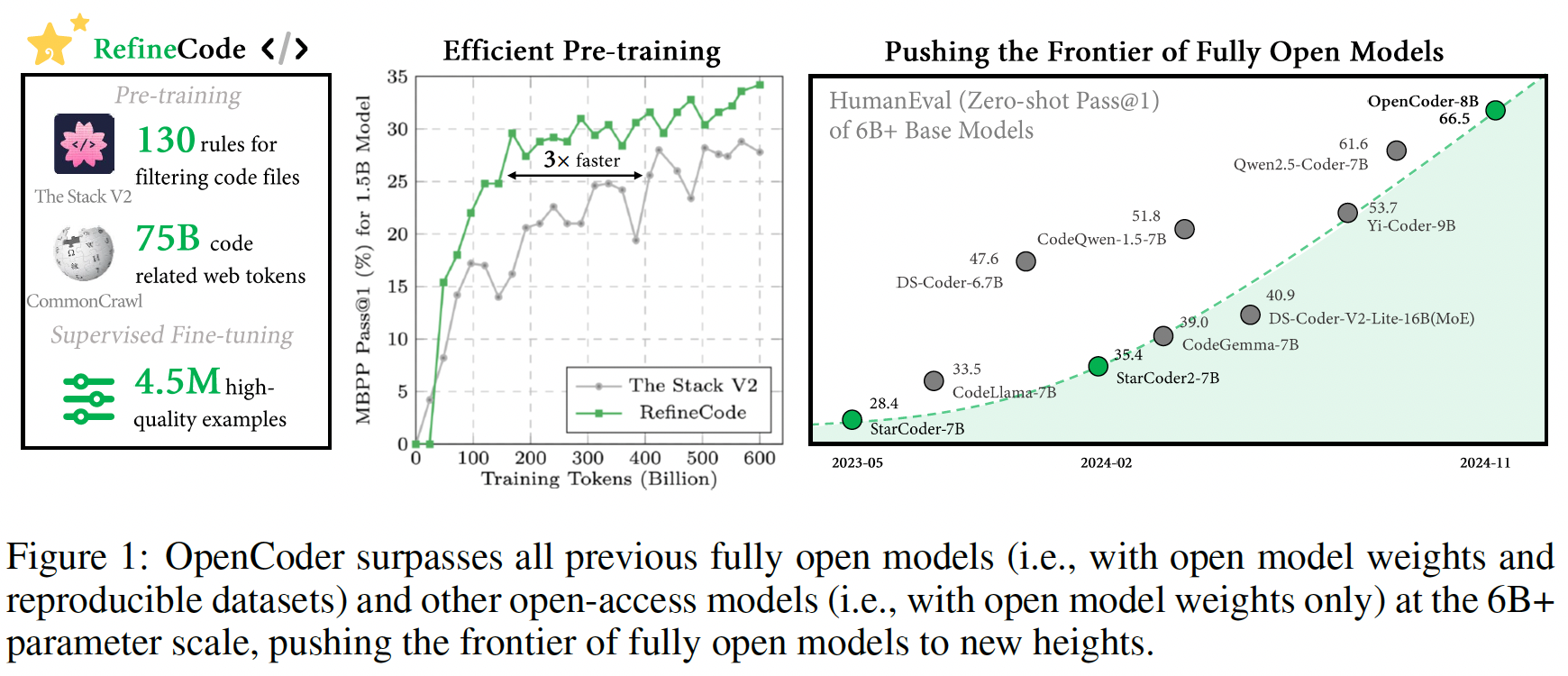
We introduce Open-Coder, a top-tier code LLM that not only achieves performance comparable to
leading models but also serves as an “open cookbook” for the research community.
Unlike most prior efforts, we release not only model weights and inference
code, but also the reproducible training data, complete data processing pipeline,
rigorous experimental ablation results, and detailed training protocols for open
scientific research.
Our key design choices for data curation:
During the pretraining phase,
the importance of data cleaning is highlighted.The impact of deduplication is significant, with file-level deduplication proving to be more effective than repository-level deduplication.
Filtering data based on Github star count can possibly reduce data diversity and affect the overall data distribution, contributing to a suboptimal result.
In the annealing phase, the use of high-quality data is crucial for further enhancing the model’s capabilities.
During the instruction tuning phase, a two-stage instruction tuning strategy is shown to be effective.
Post Training#
Data Composition#
Open-source Training Data To enhance the model training, we collect the open-source instruction corpora from the websites, including Evol-Instruct, Infinity-Instruct, McEval. Additionally, we sample real user queries from WildChat-1M and Code-290k-ShareGPT. For low-quality responses, we employ a robust LLM to regenerate the content, enhancing the overall data quality.
Educational Instruction Synthesis In synthesizing instruction-tuning datasets for Python code, we enhance the effectiveness of Magicoder[WWL+24]. Specifically, we observe that the educational value of the synthesized data largely depends on the quality of the seed data. Our approach:
Using only high-quality seed data.
Use a teacher model to generate multiple test cases for the code sections in each problem. These test cases are appended to the code snippets and executed using a Python interpreter. Only the data samples that successfully pass the tests are retained.
Package-related Instruction Synthesis Due to a significant amount of outdated package usage in the pre-training data, LLM may sometimes employ methods from older versions of libraries when generating code. To mitigate this:
Analyzed commonly used external Python libraries and retrieved API signatures and usage examples via PyDoc.
This information was sent to prompt a teacher model that generated accurate and
up-to-date question-answer pairsreflecting current usage.
Large-scale Diverse Instruction Synthesis To increase the diversity of the instruction dataset:
An LLM is used first to clean the irrelevant context in the websites and select useful sentences as the seed for further question generation.
A task specification module defines programming languages, difficulty levels, and coding task types. The prompt engineering component employs a template-based system to generate diverse, contextually rich prompts, incorporating realworld scenarios and best practices in software development. We set temperature \(T = 1.0\) for diverse questions.
An advanced LLM with more parameters first generates the created questions and then generates the corresponding answers. The validation module combines automated code execution and unit testing to check the correctness.
Tip
Similar to Magicoder, while use useful sentences in the websites as the seed.
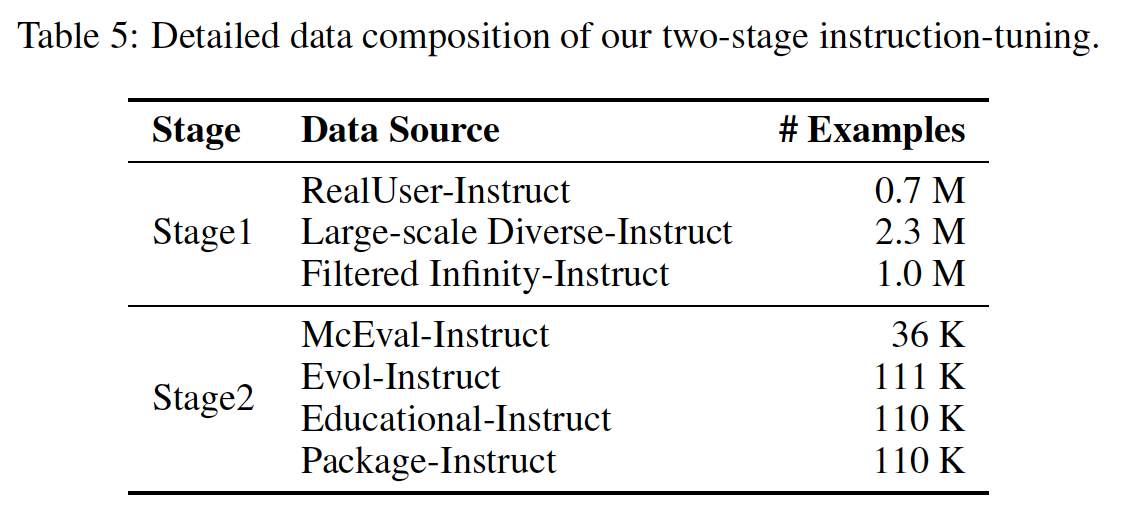
Two-stage Instruction-Tuning#
The first stage of this fine-tuning process focused on synthesizing question-answer (QA) pairs related to theoretical computer science. In the second stage of the fine-tuning process, we shifted focus from theoretical knowledge to practical coding tasks.
Training Details#
In the first stage of SFT, we trained for one epoch with a batch size of 4096, a learning rate (LR) of 2e-5, warmup steps set to 100, and a cosine learning rate scheduler. In the second stage of SFT, we trained for three epochs using a batch size of 512, a learning rate of 5e-5, with 100 warmup steps, and the same cosine learning rate scheduler.
Decontamination#
We removed any data containing
the entry points corresponding to test sets such as HumanEval and MBPP. Additionally, we performed 10-gram deduplication, removing any data with a 10-gram overlap with the test sets.
