DeepSeek-GRM#
Note
In this work, we investigate
how to improve reward modeling (RM) with more inference compute for
general queries, i.e. the inference-time scalability of generalist RM.
For the RM approach, we adopt pointwise
generative reward modeling (GRM) to enable flexibility for different input
types and potential for inference-time scaling. For the learning method,
we propose Self-Principled Critique Tuning (SPCT) to foster scalable
reward generation behaviors in GRMs through online RL, to generate principles adaptively and critiques accurately, resulting in DeepSeek-GRM
models.
Comparisons of Different RM approaches#
RM approaches are mainly determined by reward generation paradigms and scoring patterns. For reward generation paradigms, we distinguish three main approaches: scalar, semi-scalar, and generative. For scoring patterns, we distinguish two main approaches: pointwise and pairwise.
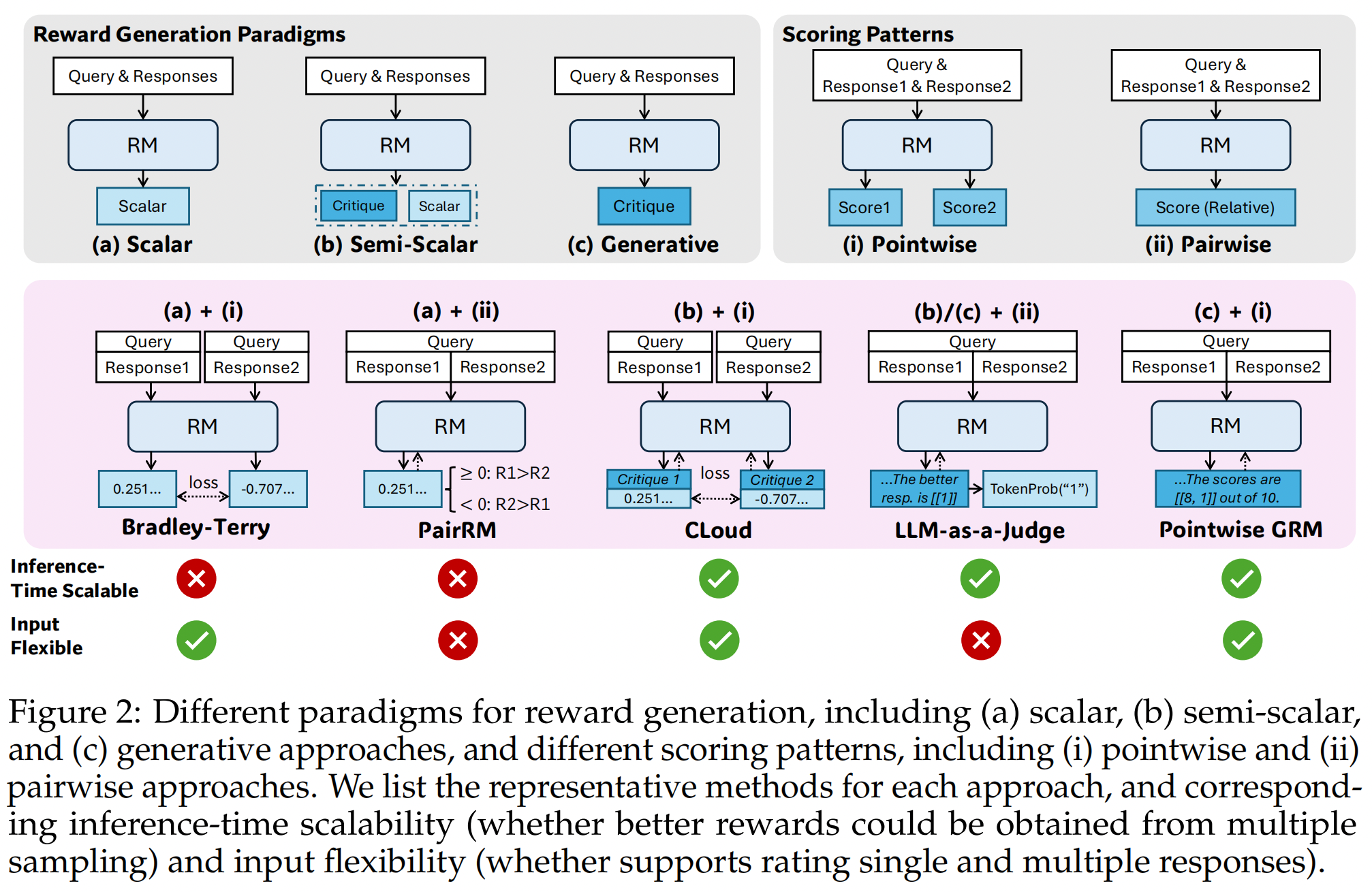
The formulation of pointwise GRMs is:
where \(x\) is the query, \(\{y_i\}\) is the \(i\)-th response, \(r_{\theta}\) is the reward function parameterized by \(\theta\), \(\mathbf{C}\) is the critique, \(S_i\) is the individual score of \(y_i\), and \(f_{\text{extract}}\) extracts the rewards from generation results.
Boosting Reward Quality with Principles#
For general domains, we adopt principles to guide reward generation in place of artificial rules. Principles for LLMs are first introduced in Constitutional AI. With principles, the reward generation of GRMs changes to
where \(\{p_{i}\}_{i=1}^{m}\) denotes the principles. We conduct a preliminary experiment to examine the influence of principles on reward quality, found that proper principles could significantly boost reward quality.
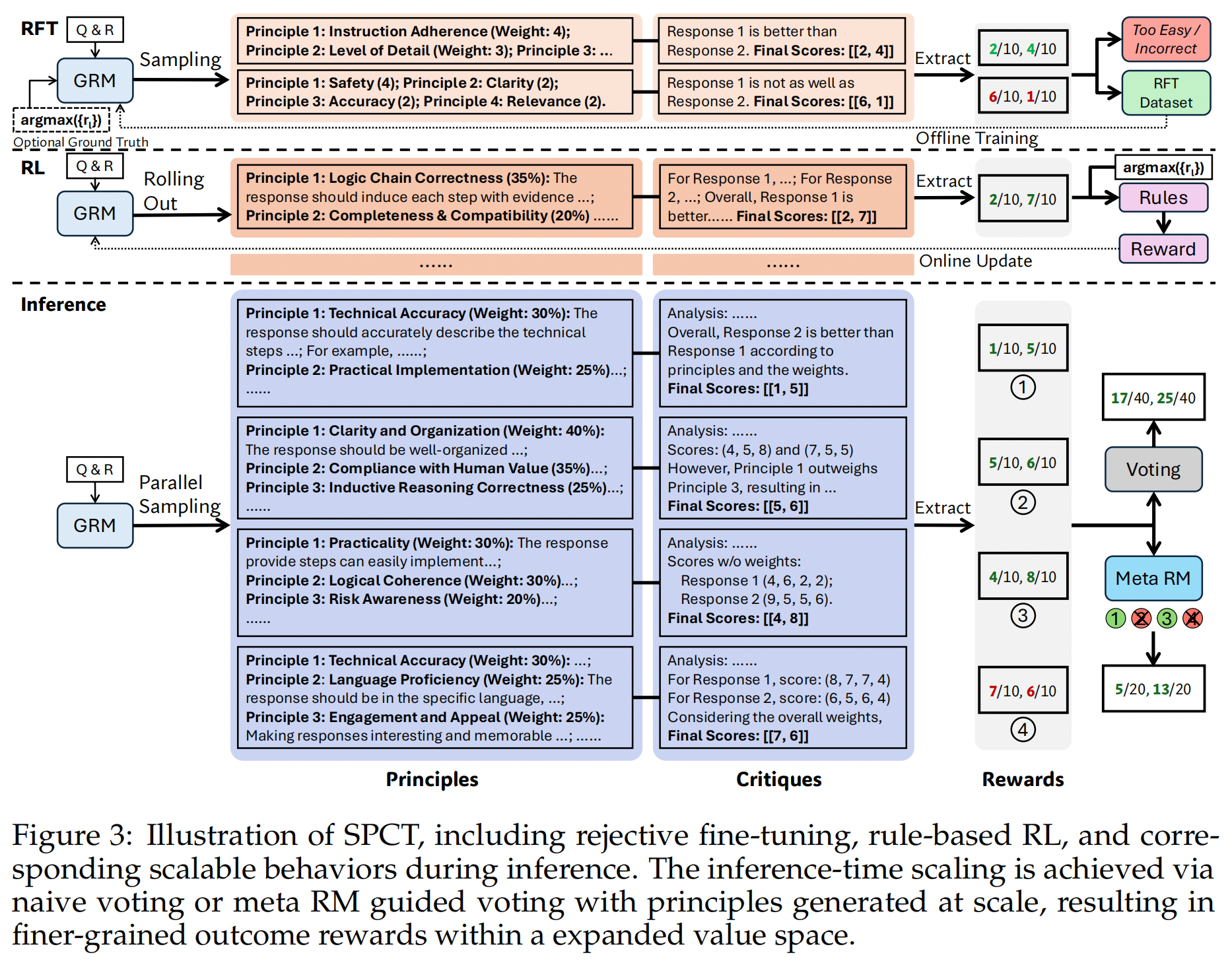
Self-Principled Critique Tuning (SPCT)#
Inspired from the preliminary results, we developed a novel approach for pointwise GRMs to learn generating adaptive and high-quality principles that could effectively guide the generation of critiques, termed Self-Principled Critique Tuning (SPCT).
Unpinning Principles from Understanding to Generation#
In the above, principles are pre-defined. GRMs could generate principles themselves, and then generate critiques based on the principles, formalized as:
This shift enables to principles to be generated based on the input query and responses, adaptively aligning reward generation process.
Rejective Fine-Tuning (Cold Start)#
To optimize principle and critique generation in GRMs simultaneously, we propose SPCT, which integrates rejective fine-tuning and rule-based RL. The former serves as a cold start.
For data construction, besides general instruction data, we sample trajectories with pretrained GRMs given the query and responses. For each query and corresponding responses, the sampling is performed \(N_{\text{RFT}}\) times. We reject trajectories with predicted rewards that are not aligned with the ground truth. Formally, let \(r_i\) denotes the ground truth reward for the \(i\)-th response \(y_i\) to the query \(x\), the predicetd pointwise rewards \(\{S_i\}_{i=1}^{n}\) are correct if
with guaranteed that the ground truth rewards only contain one maximum.
Rule-Based RL#
The GRM is further fine-tuned with rule-based online RL. Specifically, we use the original setting of GRPO with rule-based outcome rewards. Formally, the reward to the given query \(x\) and responses \(\{y_i\}_{i=1}^{n}\) is
The reward function encourages GRMs to distinguish the best responses with online optimized principles and critiques.
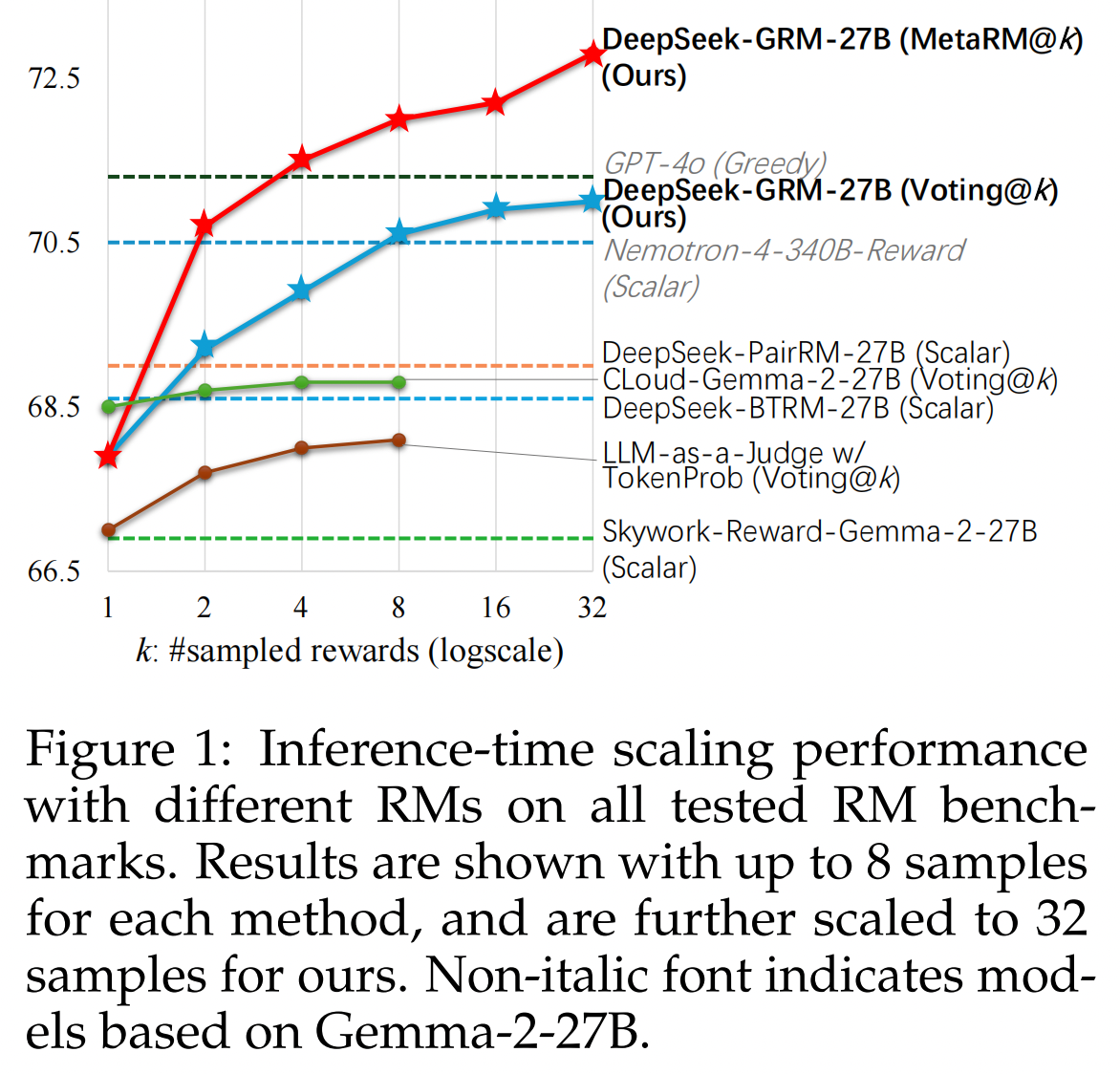
Inference-Time Scaling with SPCT#
To further improve the performance of DeepSeek-GRM for generalist reward generation using more inference compute, we explores sampling-based strategies to achieve effective inference-time scalability.
Voting with Generated Rewards. The voting process for pointwise GRMs is defined as summing the rewards:
Meta Reward Modeling Guided Voting. We train a meta RM to guide the voting process. The meta RM is a pointwise scalar RM, trained to identify the correctness of the principle and critique generated by DeepSeek-GRM, with the binary cross-entropy loss. The guided voting is simple: The meta RM outputs meta rewards for \(k\) sampled rewards, and the final outcome is voted by rewards with top \(k_{\text{meta}} ≤ k\) meta rewards, so that filtering out low-quality samples.
Results on Reward Modeling Benchmarks#