AGENTLESS#
Note
The complexity
of former agent-based approaches, together with the limited abilities of
current LLMs, raises the following question: Do we really have to employ
complex autonomous software agents?
To attempt to answer this question,
we build AGENTLESS – an agentless approach to automatically resolve
software development issues. AGENTLESS employs a simplistic three-phase
process of localization, repair, and patch validation, without letting the
LLM decide future actions or operate with complex tools.
AGENTLESS Approach#
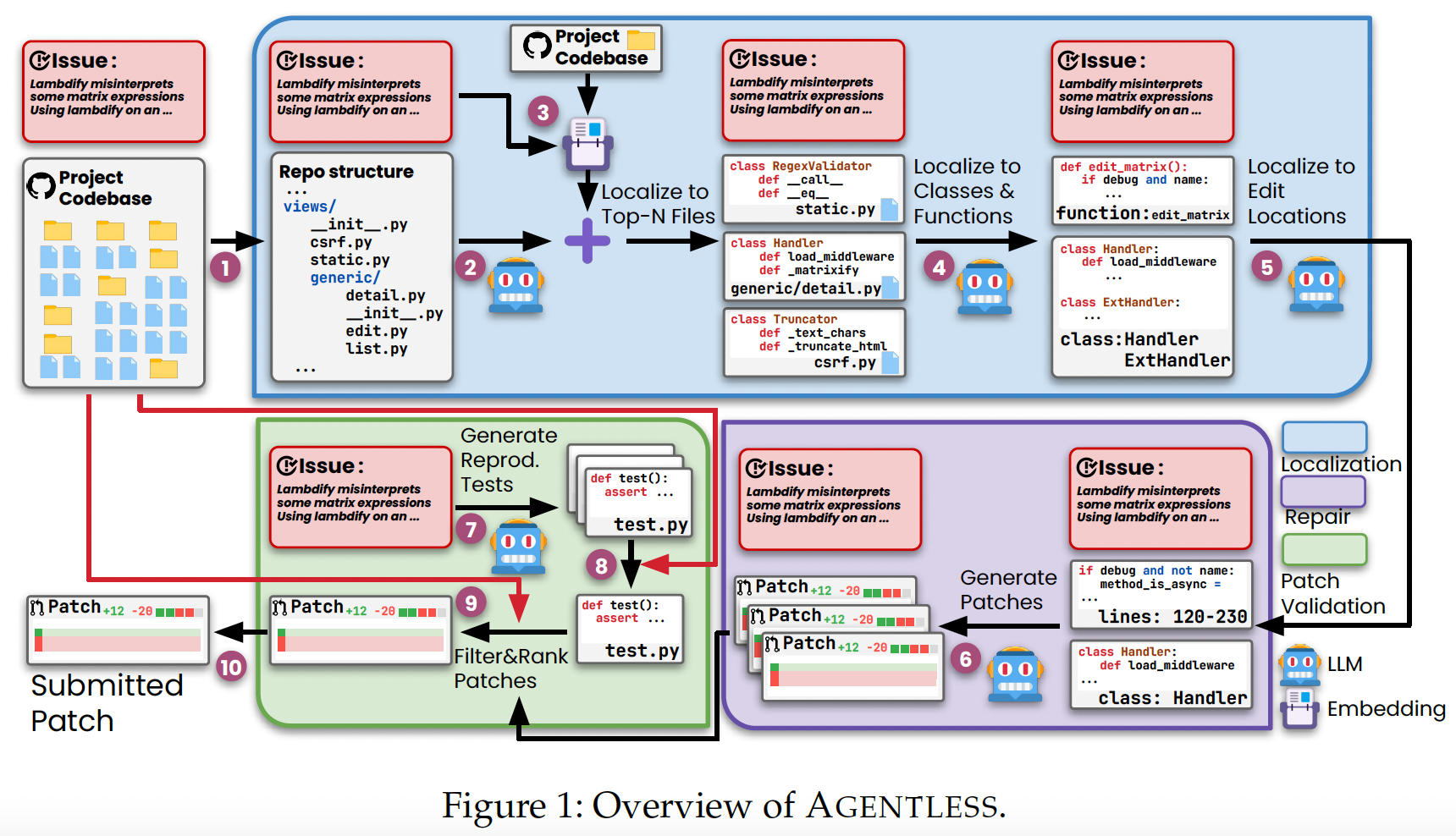
Figure 1 shows the overview of AGENTLESS, consisting of three phases: localization, repair, and patch validation.
We first take in the issue description and the existing project codebase as input. Then, we begin our hierarchical localization process by turning the project codebase into a tree-like structure that illustrates the relative location of each file in the project.
Next, using this repository structure along with the original issue description, we prompt the LLM to localize and rank the top \(N\) most suspicious files that likely require editing to solve the issue.
Since our repository structure format does not contain detailed source code information, we additionally retrieve files with most relevant code snippets with the issue description using embedding-based retrieval.
We then combine the retrieved files with the LLM-localized files to obtain the final list of suspicious files. However, not all contents in each file need to be modified. As such, we provide a skeleton for each file (i.e., a list of declaration headers of the classes and functions) and ask the LLM to output a specific list of classes and functions that we should examine more closely to fix the bug.
We then provide the complete code content of the previous locations and ask the LLM to finalize a smaller set of edit locations (i.e., classes, functions, or even specific lines).
For the
repair phase, we provide the code snippets at these edit locations together with the issue description and prompt the LLM to sample multiple patches to solve the issue.Next, we enter the patch validation phase, where we first ask the LLM to sample multiple reproduction tests that aim to replicate the original issue.
and then select the optimal one based on actual execution results on the original codebase.
AGENTLESS uses the reproduction test along with existing regression tests for patch ranking/selection.
Finally, AGENTLESS selects the top-ranked patch as the final patch for submission.
