BigCodeBench#
Note
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for solving practical and challenging tasks via code. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls.
There are two splits in BigCodeBench:
Complete: Thes split is designed for code completion based on the comprehensive docstrings.
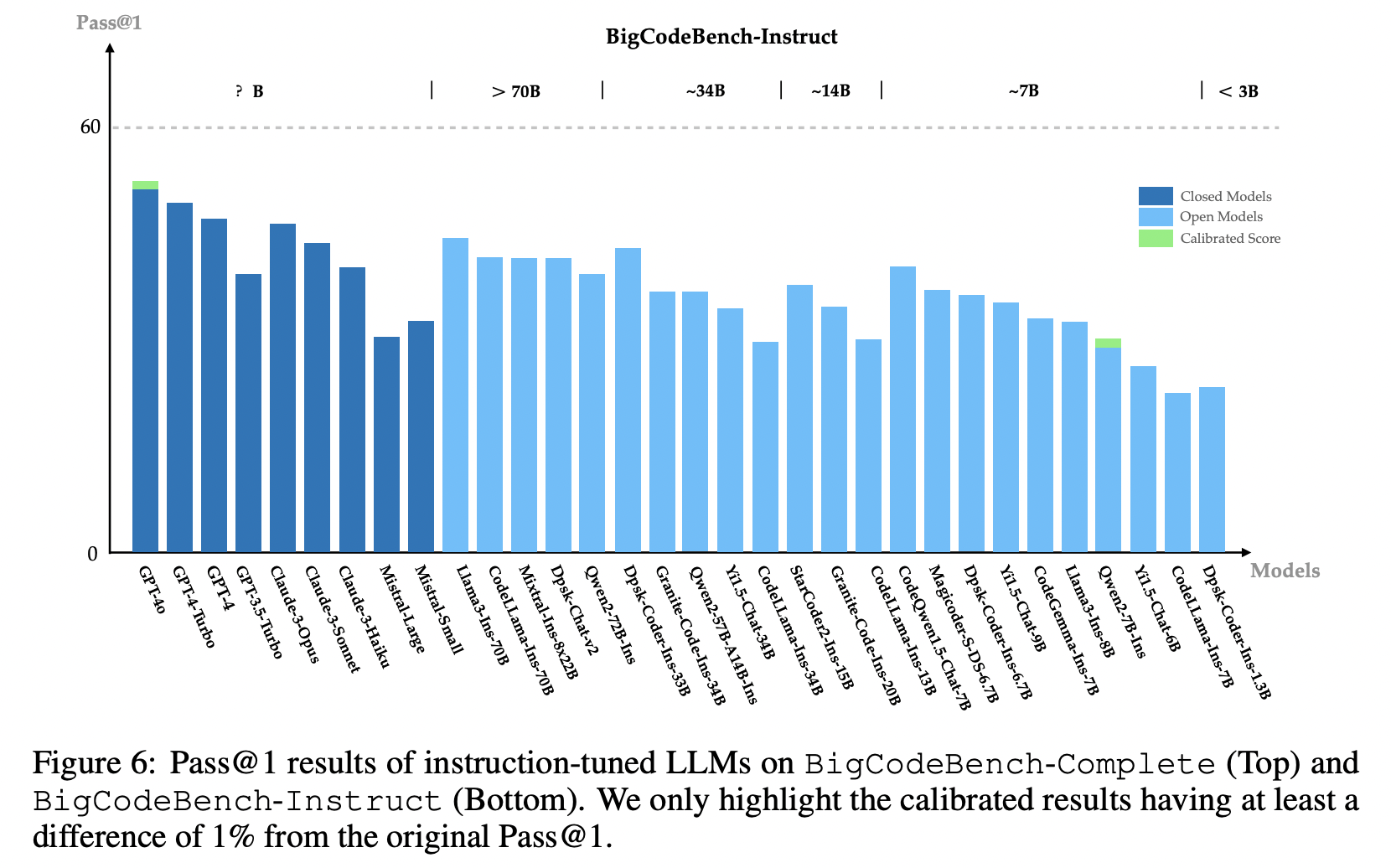
Instruct: The split works for the instruction-tuned and chat models only, where the models are asked to generate a code snippet based on the natural language instructions.
Benchmark Construction#
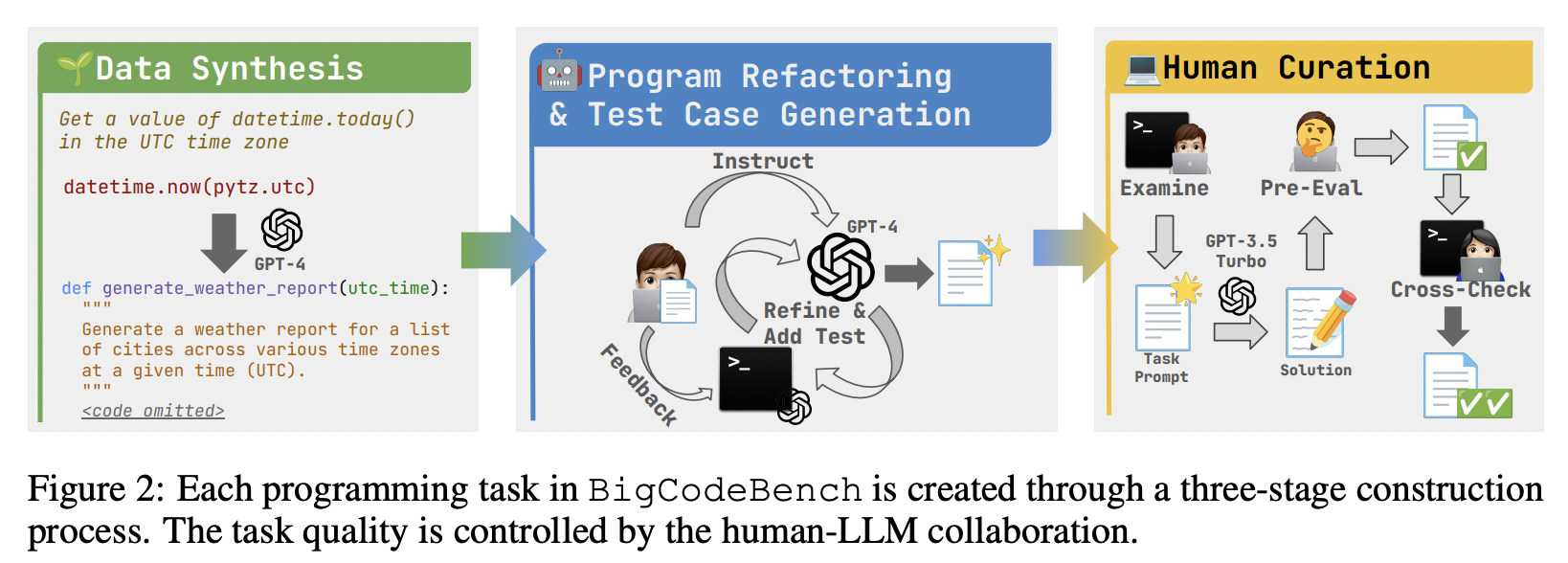
Data Synthesis#
Given a code snippet of API usage with a brief human instruction as the seed example, an LLM is instructed to enrich the programming intent and refine the corresponding implementation by using diverse libraries. We instruct the model with a 2-shot in-context demonstration.
Semi-Automatic Program Refactoring and Testing Case Generation#
Programs synthesized by LLMs may contain various issues, without proper verification, the implementation cannot directly serve as a ground-truth solution. To construct a high-quality execution-based benchmark, we need to add test cases that can rigorously verify the correctness of programs and identify any bugs.
Human Curation#
To enhance the benchmark quality, we implement a three-fold human curation process:
Examination
Pre-Evaluation
Cross-Checking
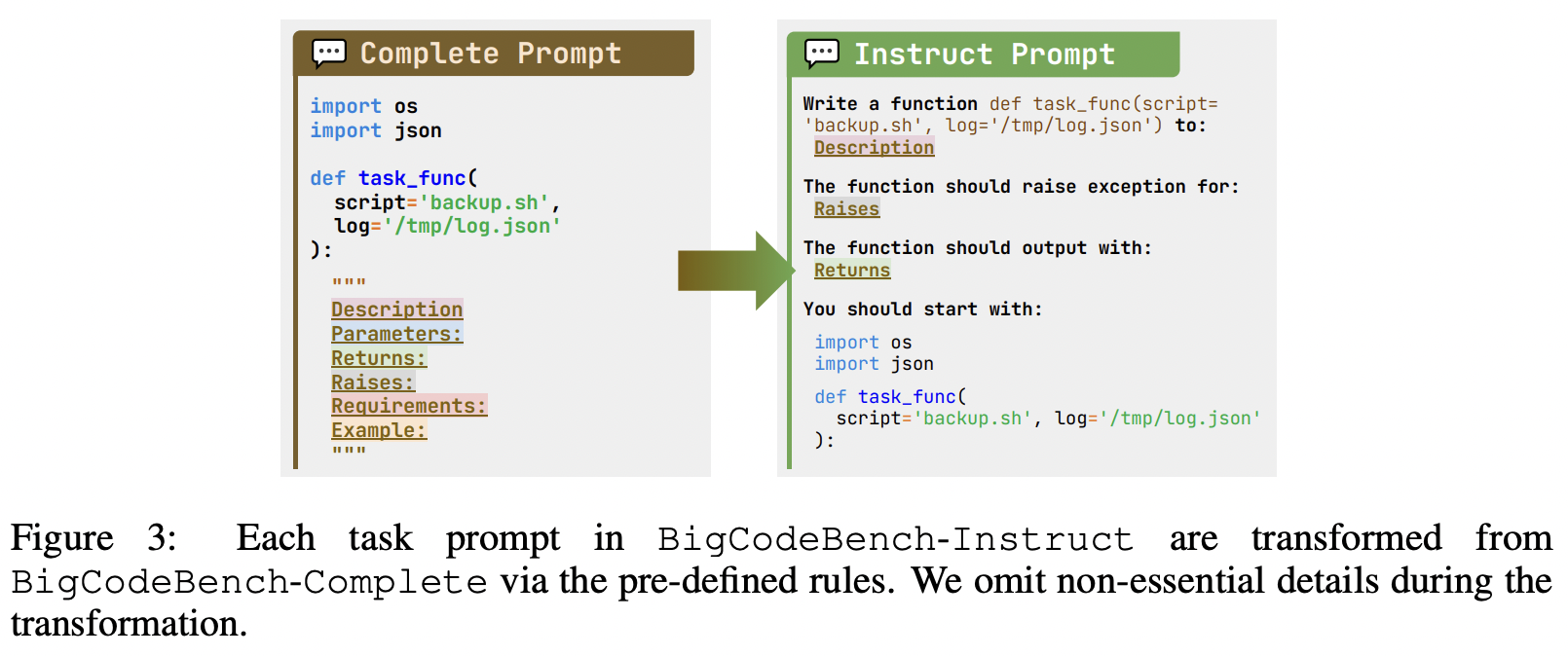
Benchmarking NL-Oriented Instructions to Code Generation#
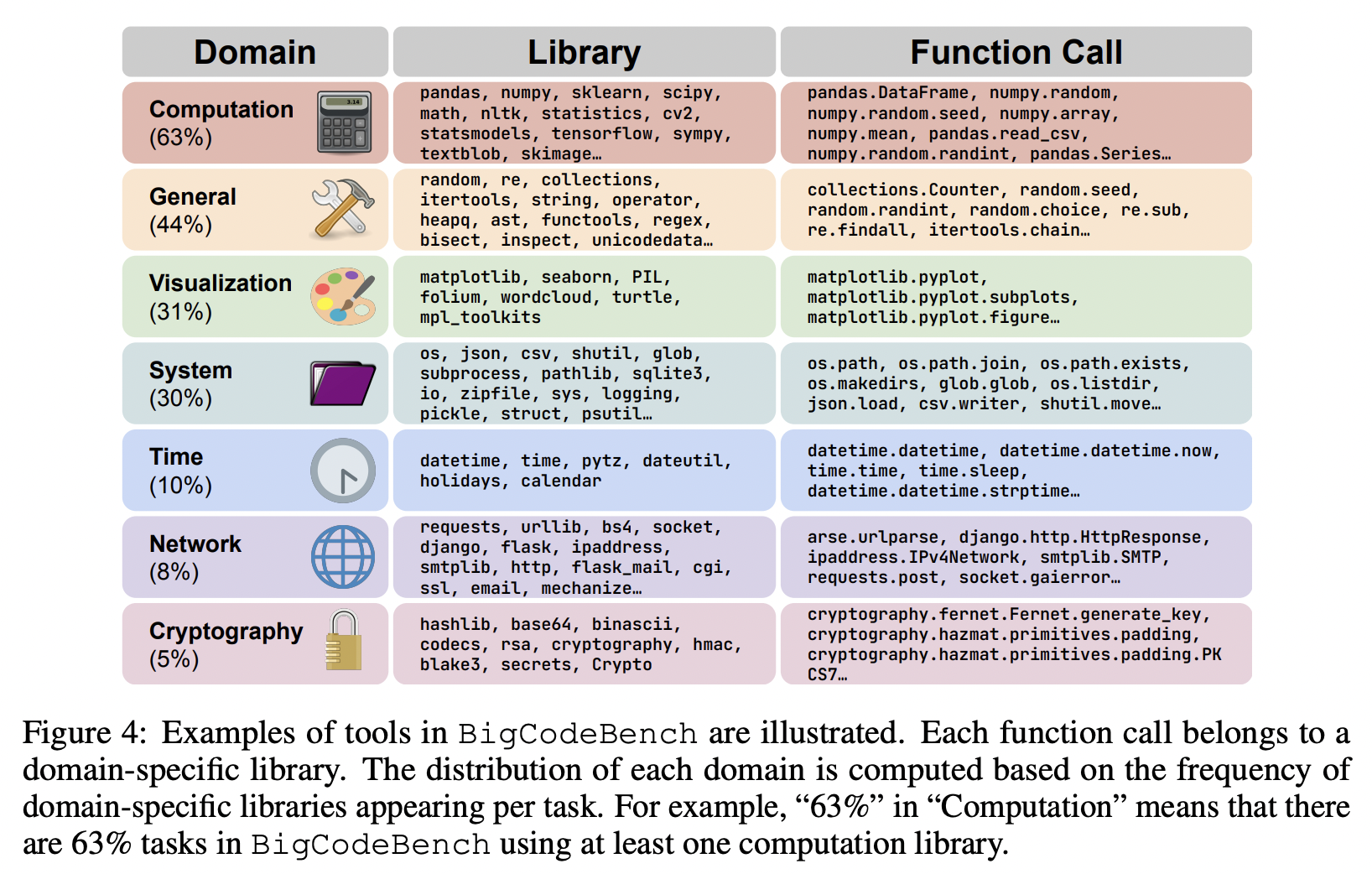
Benchmark Statistics#
Evaluation#
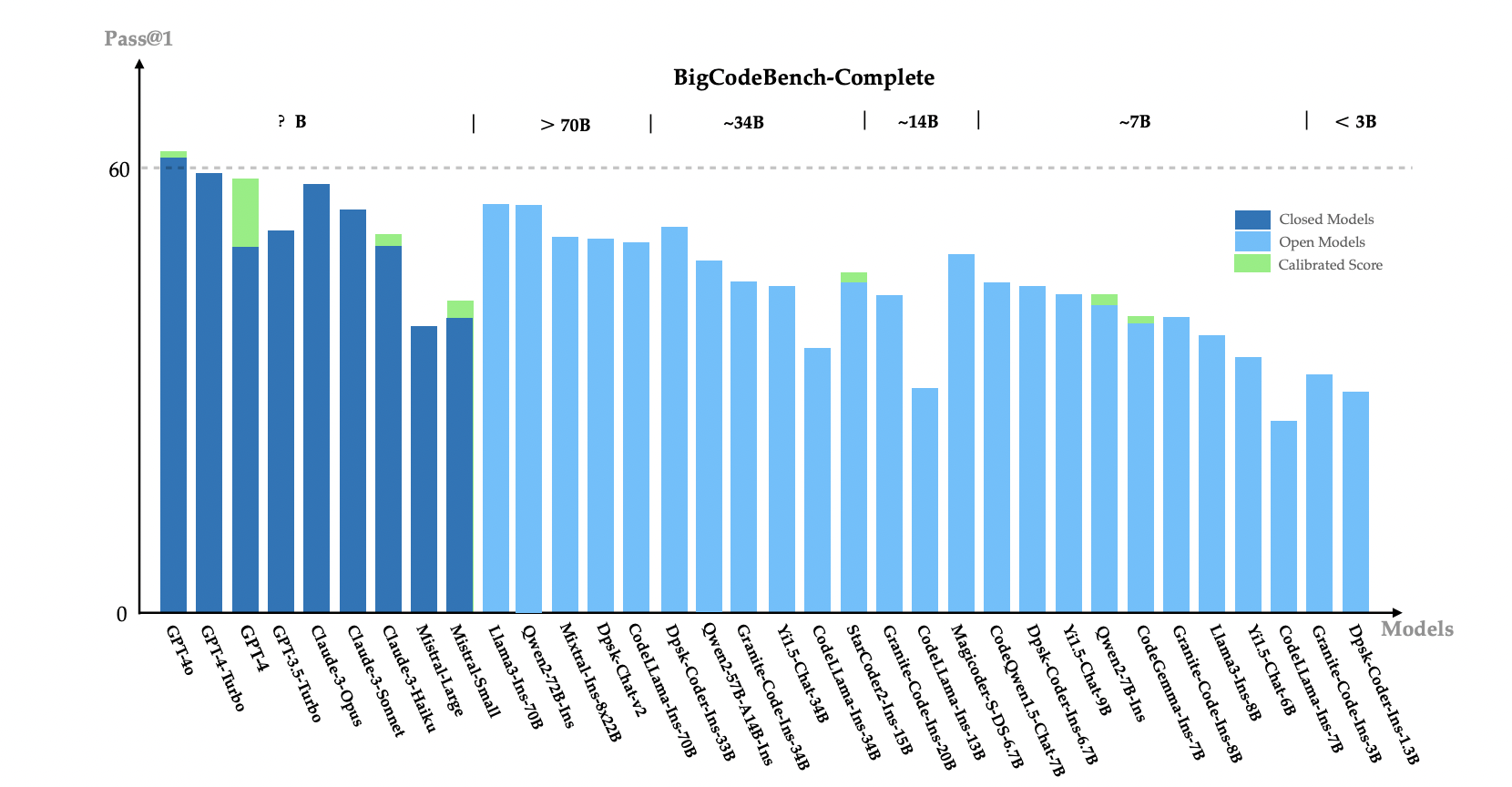
Our extensive evaluation of 60 LLMs shows that LLMs are not yet capable of following complex instructions to use function calls precisely, with scores up to 60%, significantly lower than the human performance of 97%.
Tip
from titlecase import titlecase
s = "BENCHMARK CONSTRUCTION"
print(titlecase(s))
