SWE-smith#
Note
Despite recent progress in Language Models (LMs) for software engineering,
collecting training data remains a significant pain point.
To address this pain point, we introduce
SWE-smith, a novel pipeline for generating software engineering
training data at scale. Given any Python codebase, SWE-smith constructs a
corresponding execution environment, then automatically synthesizes 100s
to 1,000s of task instances that break existing test(s) in the codebase.
SWE-smith: Software Task Generation at Scale#
Building execution environments for repositories with passing tests. Given a repository, we run SWE-agent on the latest commit for at most 100 steps, instructing it to install the codebase and run the test suite. We then manually verify the installation and testing instructions, check if more than 80% of existing tests pass, and finally create a Docker image for the repository.
Creating task instance candidates. we employ four different strategies to create candidates
LM Generation: Per repository, we identify all programmatic entities (functions, classes), then take two approaches: (1) provide anLM with the function and prompt it to introduce errant modifications (henceforth referred to as “LM Modify”), and (2) given only the function header and docstring, ask the LM to rewrite it (“LM Rewrite”).
Procedural Modification: Per function, we acquire an abstract syntax tree (AST) representation of the code, then randomly perform one or more transformations.
Combine Bugs: To create more complex tasks that require editing multiple portions of the codebase, we devise a “Patch Combination” strategy that creates a task instance by aggregating candidates from the same file(s) or module(s).
Invert PRs: Per repository, we collect all PRs that modify Python files. Per PR, we attempt to undo its revisions in the current version of the repository.
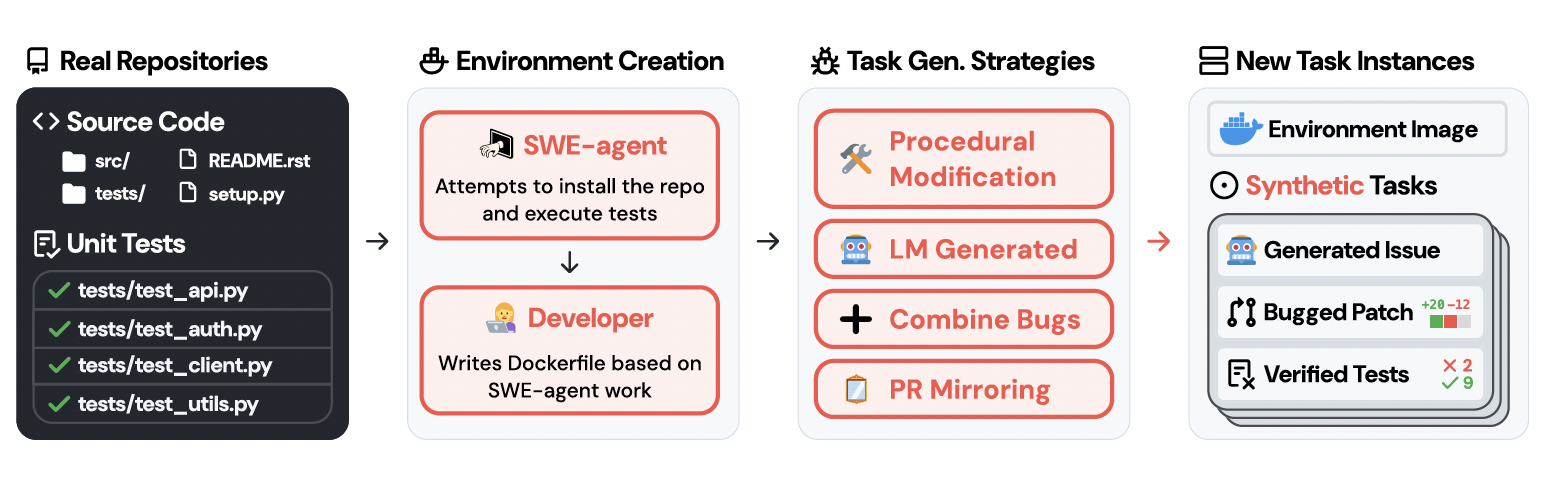
Execution-based validation of candidates. We apply each candidate patch to the corresponding repository, run the test suite, and only keep patches that break one or more existing, passing tests (referred to as Fail-to-Pass or F2P test(s)).
Generating problem statements. Per task instance, we provide an LM with the .diff patch, source code of a random F2P test, and execution output from running the repository’s test suite with the bug patch applied. We prompt the LM for GitHub issue-style text that includes reproduction code based on the F2P test.
Tip
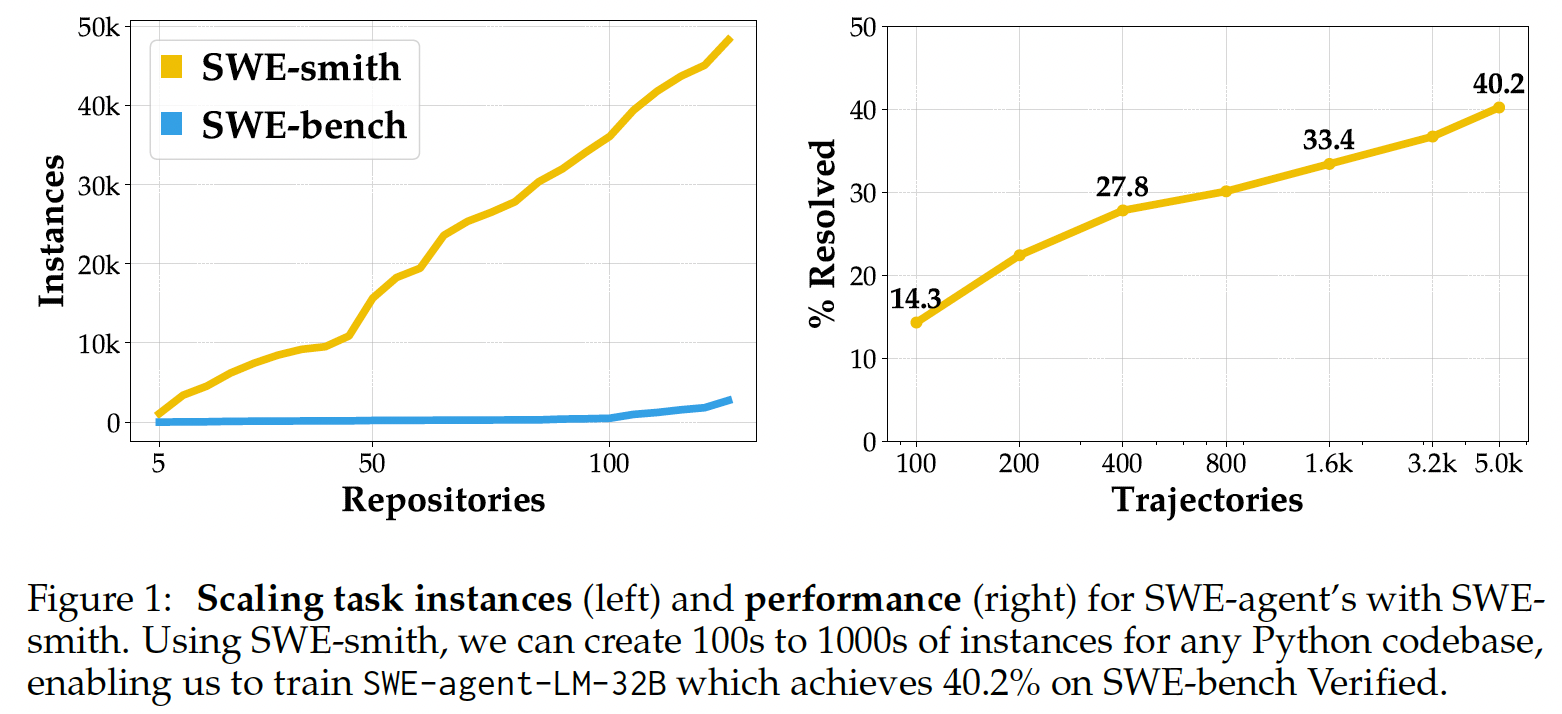
Using SWE-smith, we create a dataset of 50k instances sourced from 128 GitHub repositories, an order of magnitude larger than all previous works. We train SWE-agent-LM-32B, achieving 40.2% Pass@1 resolve rate on the SWE-bench Verified benchmark, state of the art among open source models.
