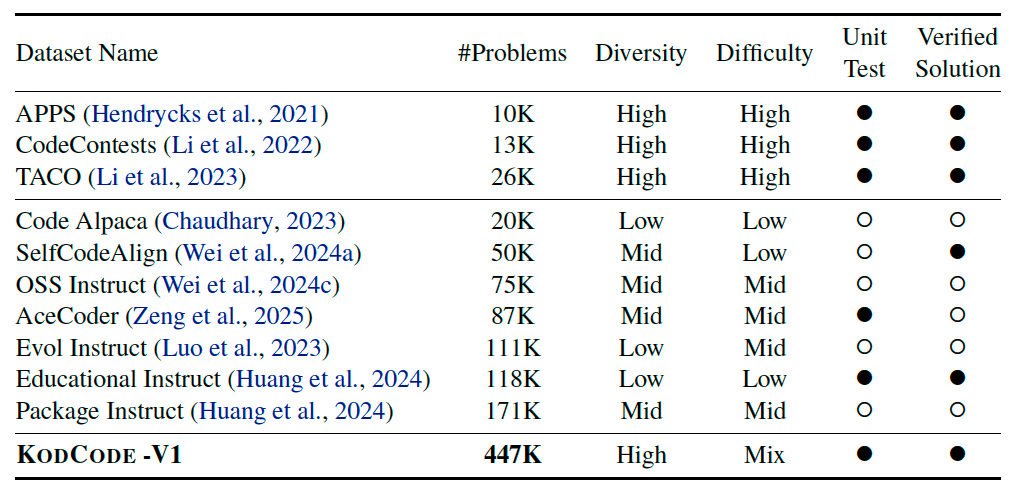
KodCode#
Note
A Diverse, Challenging, and Verifiable Synthetic Dataset for Coding.
Step 1: Coding Question Synthesis#
Simple Coding Questions. We extend the MAGPIE framework and introduce MAGPIE-Prefill. This approach generates simple coding
questions by prefilling the user message in the chat
template with a pre-defined suffix (e.g., “Write a
Python function that”), and leverages Qwen2.5-
Coder-7B-Instruct to complete the remaining part
of the user query.
Coding Assessment Questions. We leverage existing human-written coding assessment datasets (e.g. TACO) as seed corpora, then we employ GPT-4o-0513 as a teacher LLM to generate new assessment questions that maintain consistency in difficulty and scope.
Data Structures and Algorithms. To fully encompass Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) knowledge, we prompt LLM to craft questions based on uniformly sampled Python DSA code snippets.
Technical Documentations. Prompt LLM to transforms technical documentation from popular Python libraries—including flask, pandas, pytorch, scikit, and seaborn—into coding questions.
More Questions. We further expand coding
questions by employing MAGPIE using seven open-source LLMs. In addition,
we synthesize more questions from existing Package Instruct and Evol Instruct.
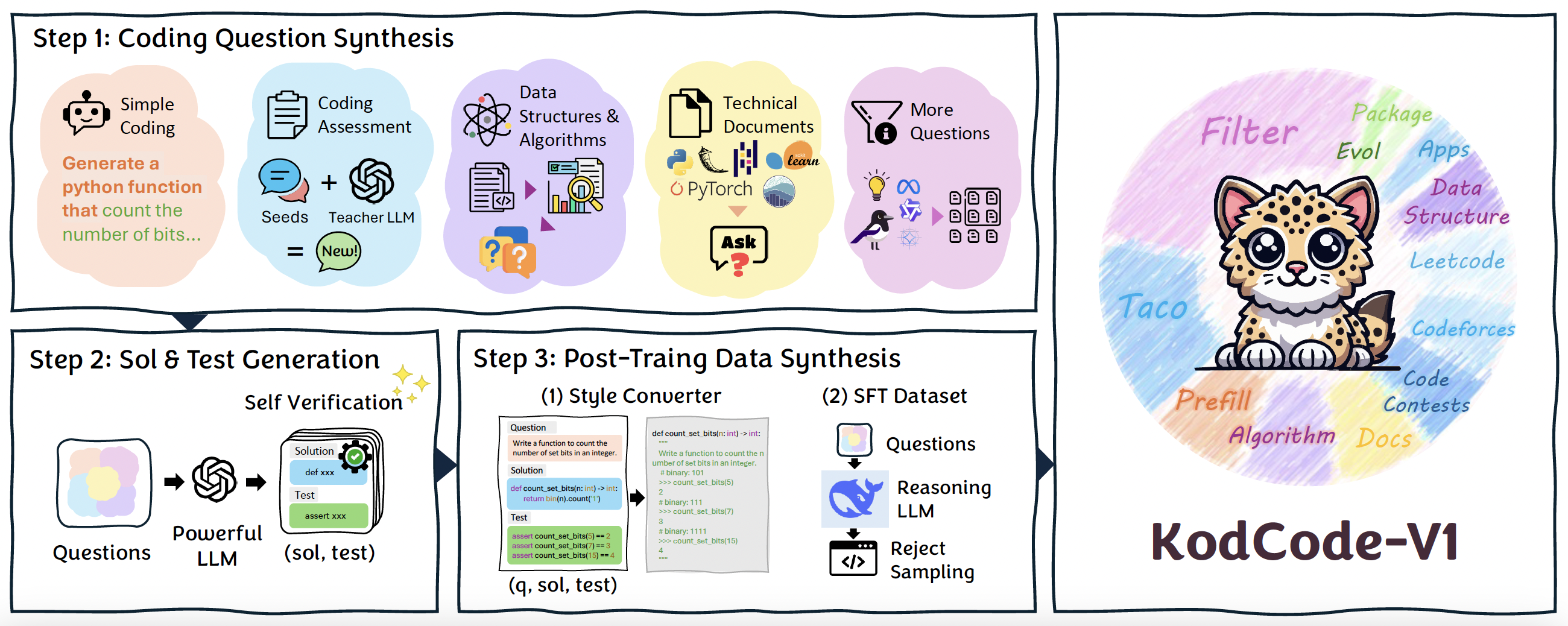
Step 2: Solution & Test Generation#
We first employ GPT-4o-0513 to generate both solution and test, then execute these unit tests to validate the correctness of the solution.
For each question from Step 1, we allow up to a maximum of \(n\) attempts (where \(n = 10\) in our experiments) to generate a solution that passes its unit tests. Importantly, each attempt fixes the question and regenerates both the solution and its corresponding unit tests from scratch. Only question-solution-test triplets that pass self-verification are retained.
Step 3: Post-training Data Synthesis#
We reformat each question \(q\) by taking its solution and test as inputs, \(q' = \text{LLM}(q, sol, test)\), structuring them as Python completion tasks with function signatures and examples (similar to HumanEval).
Motivated by recent advances in reasoning models, we further generate an SFT dataset for post-training using DeepSeek R1.
