Qwen3#
Note
The Qwen3 series includes models of both dense and Mixture-of-Expert (MoE) architectures, with parameter scales ranging from 0.6 to 235 billion. A key innovation in Qwen3 is the integration of thinking mode (for complex, multi-step reasoning) and non-thinking mode (for rapid, context-driven responses) into a unified framework.
Architecture#
The architecture of the Qwen3 dense models is similar to Qwen2.5, we remove QKV-bias used in Qwen2 and introduce QK-Norm to the attention mechanism to ensure stable training for Qwen3. Unlike Qwen2.5-MoE, the Qwen3-MoE design excludes shared
experts. Furthermore, we adopt the global-batch load balancing loss to encourage expert
specialization.
Pre-training#
Pre-training Data. Compared with Qwen2.5, we have significantly expanded the scale and diversity of our training data.
Pre-training Stage.
General Stage
Reasoning Stage
Long Context Stage
Post-training#
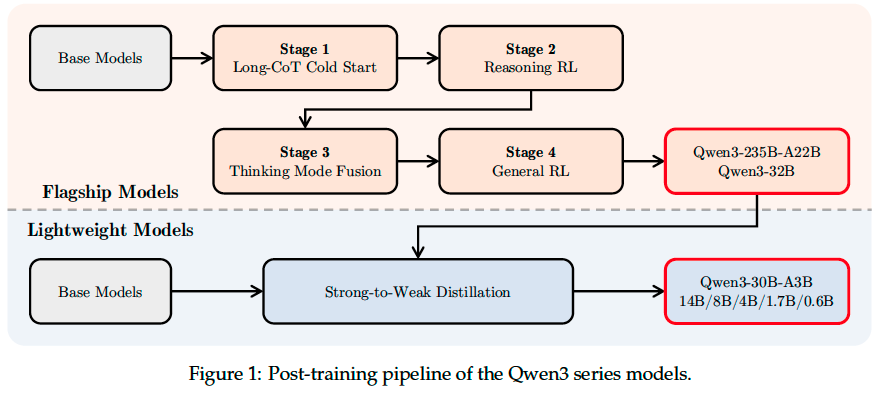
As illustrated in Figure 1, the flagship models in the Qwen3 series follow a sophisticated four-stage training process. The first two stages focus on developing the models’ “thinking” abilities. The next two stages aim to integrate strong “non-thinking” functionalities into the models.
Long-CoT Cold Start#
We begin by curating a comprehensive dataset that spans a wide range of categories, including math, code, logical reasoning, and general STEM problems. Each problem in the dataset is paired with verified reference answers or code-based test cases.
The dataset construction involves a rigorous two-phase filtering process: query filtering and response filtering.
We use Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct to identify and remove queries that are not easily verifiable. Furthermore, we exclude queries that Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct can answer correctly without using CoT reasoning. Additionally, we annotate each query’s domain using Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct to maintain balanced domain representation across the dataset.
After reserving a validation query set, we generate \(N\) candidate responses for each remaining query using QwQ-32B. For queries with positive \(Pass@N\), further stringent filtering criteria are applied.
The objective at this stage is to instill foundational reasoning patterns in the model without overly emphasizing immediate reasoning performance.
Reasoning RL#
The query-verifier pairs used in the Reasoning RL stage must satisfy the following four criteria:
They were not used during the cold-start phase.
They are learnable for the cold-start model.
They are as challenging as possible.
They cover a broad range of sub-domains.
We ultimately collect a total
of 3,995 query-verifier pairs, and employed GRPO to update the model parameters. We observe that using a large batch size and a high number of rollouts per query, along with off-policy
training to improve sample efficiency, is beneficial to the training process. We have also addressed how
to balance exploration and exploitation by controlling the model’s entropy to increase steadily or remain stable, which is crucial for maintaining stable training.
Caution
off-policy? How to balance exploration and exploitation by controlling the model’s entropy?
Thinking Mode Fusion#
Construction of SFT data. The SFT dataset combines both the “thinking” and “non-thinking” data. The “thinking” data is generated via rejection sampling on Stage 1 queries using the Stage 2 model itself. The “non-thinking” data, on the other hand, is carefully curated to cover a diverse range of tasks, we employ automatically generated checklists for assessing the response quality of “non-thinking” data.
Chat Template Design.
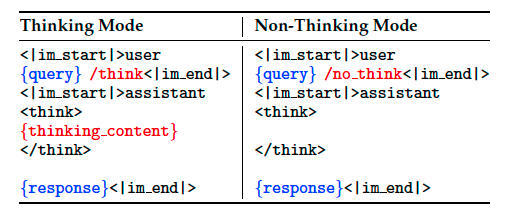
Thinking Budget. An additional advantage of Thinking Mode Fusion is that, once the model learns to respond in both non-thinking and thinking modes, it naturally develops the ability to handle intermediate cases—generating responses based on incomplete thinking. Specifically, when the length of the model’s thinking reaches a user-defined threshold, we manually halt the thinking process and insert the stop-thinking instruction: “Considering the limited time by the user, I have to give the solution based on the thinking directly now.\n.\n\n”.
General RL#
The General RL stage aims to broadly enhance the models’ capabilities and stability across diverse scenarios. To facilitate this, we have established a sophisticated reward system covering over 20 distinct tasks, each with customized scoring criteria. We utilized three distinct types of rewards:
Rule-based Reward
Model-based Reward with Reference Answer
Model-based Reward without Reference Answer
Strong-to-Weak Distillation#
The Strong-to-Weak Distillation pipeline is specifically designed to optimize lightweight models, the distillation process is divided into two primary phases:
Off-policy Distillation: At this initial phase, we combine the outputs of teacher models generated with both /think and /no_think modes for response distillation.
On-policy Distillation: In this phase, the student model generates on-policy sequences for fine-tuning. Specifically, prompts are sampled, and the student model produces responses in either /think or /no_think mode. The student model is then fine-tuned by aligning its logits with those of a teacher model (Qwen3-32B or Qwen3-235B-A22B) to minimize the KL divergence.
