Instag#
Note
We propose INSTAG, an open-set fine-grained tagger, to tag samples within SFT datasets based on semantics and intentions
Instag#
Open-Set Fine-Grained Tagging#
We use the prompt shown in Tab. 4 to employ CHATGPT, providing fine-grained intention tags for given queries. The number of original tags annotated by CHATGPT is larger than 12K, showing CHATGPT can provide diverse and fine-grained annotations. However, we notice the original tagging results provided by CHATGPT contain noticeable noises, including inconsistency in word format and granularity. Therefore, we design a systematic method to normalize the open-set tagging results from CHATGPT.

Tag Normalization#
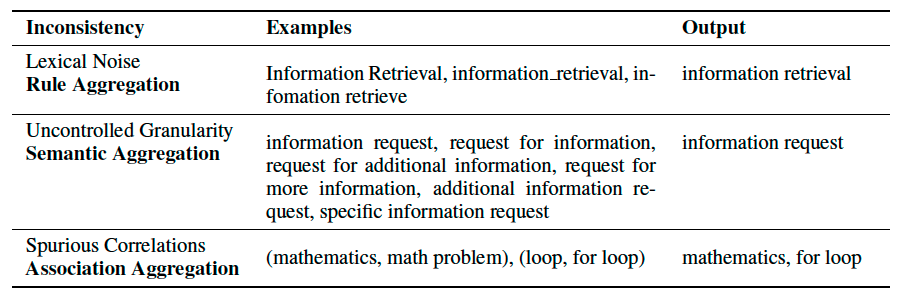
We have identified three significant types of noise. We normalize the raw tagging results with the following normalization procedure:
Frequency Filtering: We first filter out long-tail tags appearing less than \(\alpha\) times in the whole annotated dataset.
Rule Aggregation: We transform all tags into lower characters and replace all special characters into spaces to further aggregate the tags. Finally, we apply stemming to each tag with the support of
NLTK.Semantic Aggregation: We employ text embedding models to obtain the semantics of tags. We use
PHRASEBERT, a BERT-based model designed explicitly for embedding phrases, such as titles of tags. Then we useDBSCANalgorithm to cluster tags with a given threshold \(t\) of semantic similarity.Association Aggregation: We analyze all raw tagging results and employ the
FP-Growthalgorithm to mine association rules between tags. We then recursively merge associated tags based on the above association rules and reduce verbosity.
Tip
FP-Growth(Frequent Pattern Growth,频繁模式增长)算法是一种高效的频繁项集挖掘算法,由韩家炜等人提出,用于从大规模数据集中发现频繁出现的项集(如交易数据中经常一起购买的商品组合)。与传统的 Apriori 算法相比,它无需生成候选集,通过构建紧凑的数据结构(FP 树)实现高效挖掘,尤其适用于海量数据场景。
Quality Evaluation#
We employ both GPT-4 and human annotators to provide judgments in a set of randomly sampled tagging results. We evaluate the quality of the normalized tagging dataset in precision and consistency:
Precision. We define precision as whether tags assigned to a specific query are all correctly related to query intentions.
Consistency. An annotation case \((t,\mathcal{I})\) contains a tag \(t\) and a set of randomly selected instructions \(\mathcal{I}\) annotated with such tag. Annotators are required to identify any semantic changes in tags across all instructions.
Preliminary Analysis#
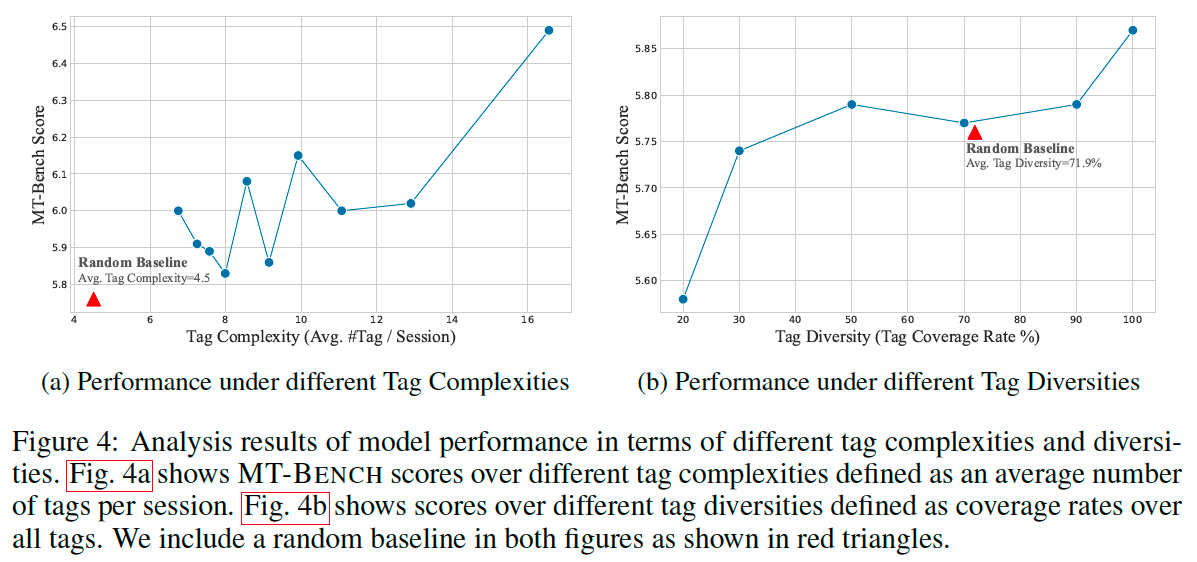
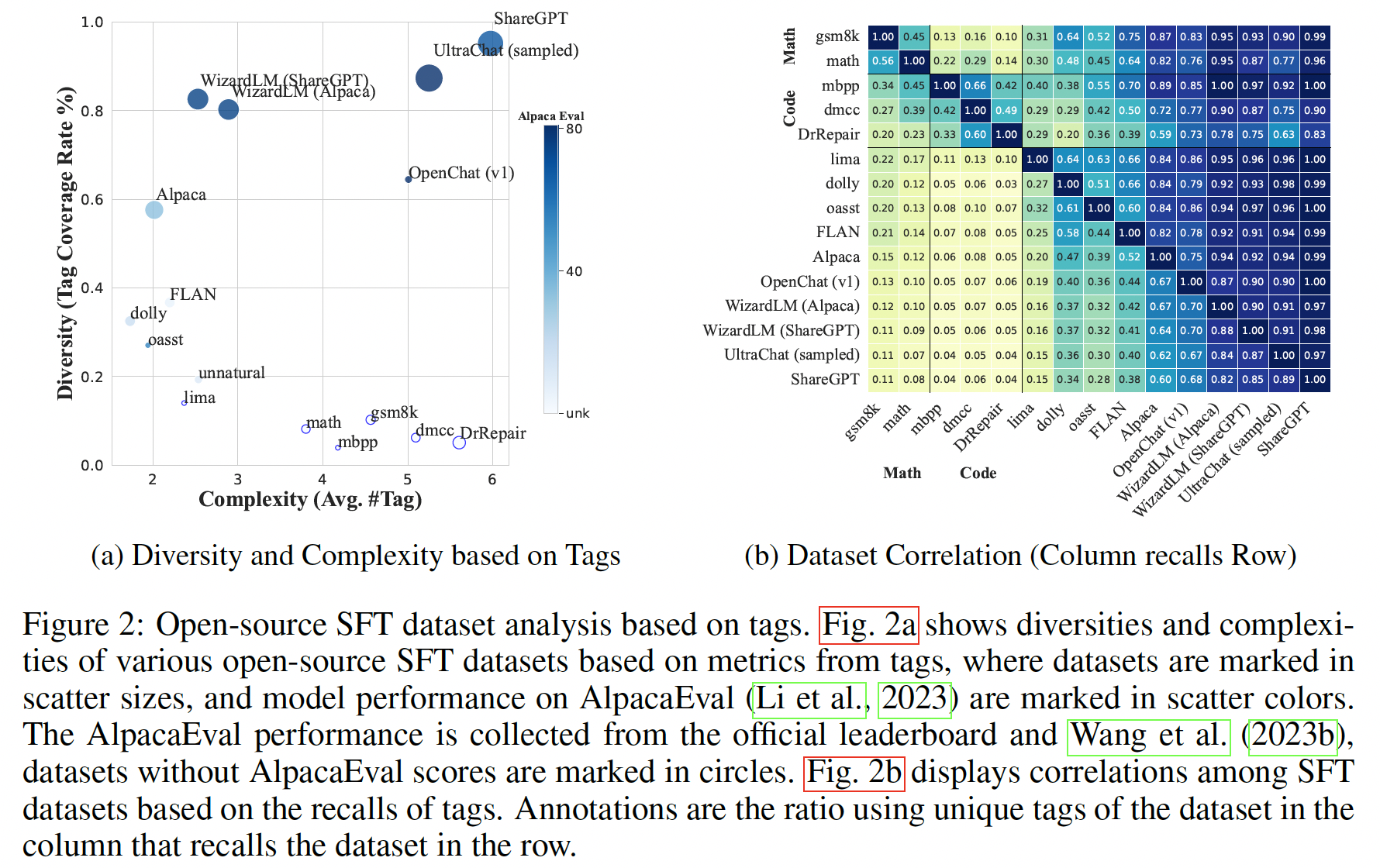
Diversity is used to access the range of intentions and semantics covered by queries in a dataset.
Complexity is quantified as the average tag number assigned to queries in a dataset.
Instag for Data Selection#
Experiment Setup#
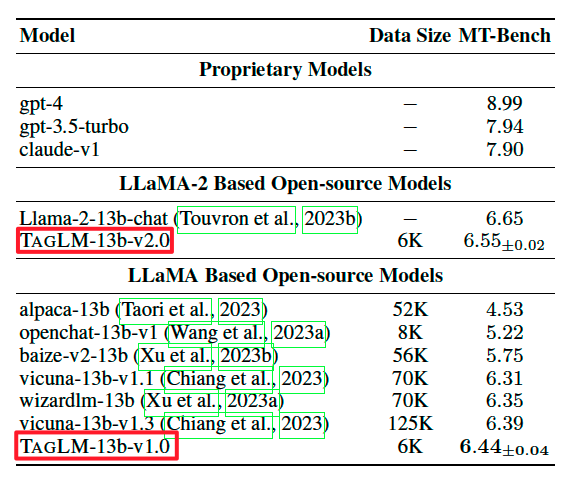
WizardLM(Alpaca), WizardLM(ShareGPT), UltraChat, and ShareGPT, these four datasets have the largest average tag numbers. We pool the four datasets, then sample an SFT data subset of 6K samples from the pooled dataset with the highest sample complexity of an average tag number 16.56 and tag coverage of 100%.
Results#
Decoupled Analysis of Complexity and Diversity#