SWE-agent#
Note
Just as humans benefit from powerful software applications, such as integrated development environments, for complex tasks like software engineering, we posit that LM agents represent a new category of end users with their own needs and abilities, and would benefit from specially-built interfaces to the software they use.
The Agent-Computer Interface#
We refer to the interface LM agents use to interact with computers as the agent-computer interface (ACI). Figure 2 illustrates how ACIs provide LM agents with important functionality to interface with computers, similar to how code editors also help humans use computers more effectively.
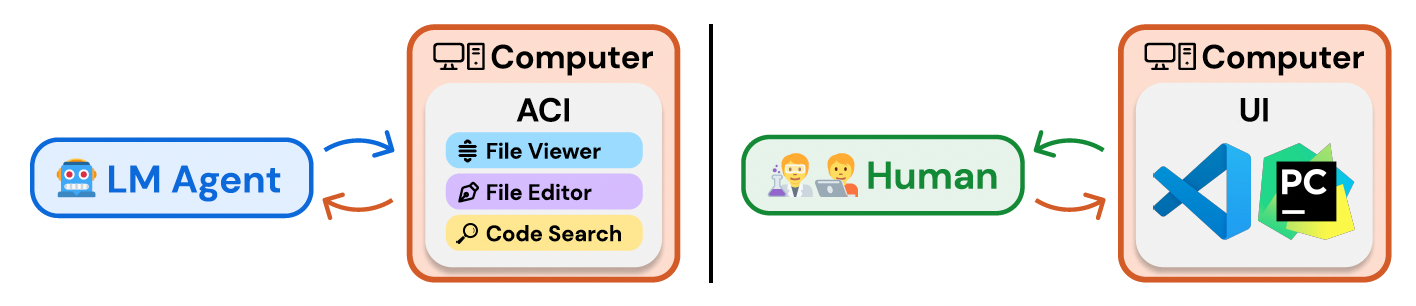
A well-designed ACI should help the LM agent understand the state of the application given previous changes, manage history to avoid unnecessary context from prior observations, and provide actions that models can use efficiently and reliably. Several insights about design principles that seem especially important for building effective ACIs:
Actions should be simple and easy to understand for agents.
Actions should be compact and efficient.
Environment feedback should be informative but concise.
Guardrails mitigate error propagation and hasten recovery. Like humans, LMs make mistakes when editing or searching and can struggle to recover from these errors. Building in guardrails, such as a code syntax checker that automatically detects mistakes, can help agents recognize and quickly correct errors.
SWE-agent: Designing an ACI for Software Engineering#
Search and navigation. We introduce the special commands find_file,
search_file, and search_dir. The find_file command searches for filenames in the repository, while the
search_file and search_dir locates strings in a file(s) of a subdirectory.

File viewer. After finding a file they want to view, agents use the interactive file viewer by calling
the command open on the relevant file path. The file viewer presents a window of at most 100
lines of the file at a time. The agent can move this window with the commands scroll_down and
scroll_up or access a specific line with the goto command.
File editor. The edit command
works in conjunction with the file viewer, allowing agents to replace a specific range of lines in the
open file.
Context management. The SWE-agent system uses informative prompts, error messages, and history processors to keep agent context concise and informative. At each step, the system instructs them to generate both a thought and an action. Malformed generations trigger an error response, asking the agent to try again, which is repeated until a valid generation is received.
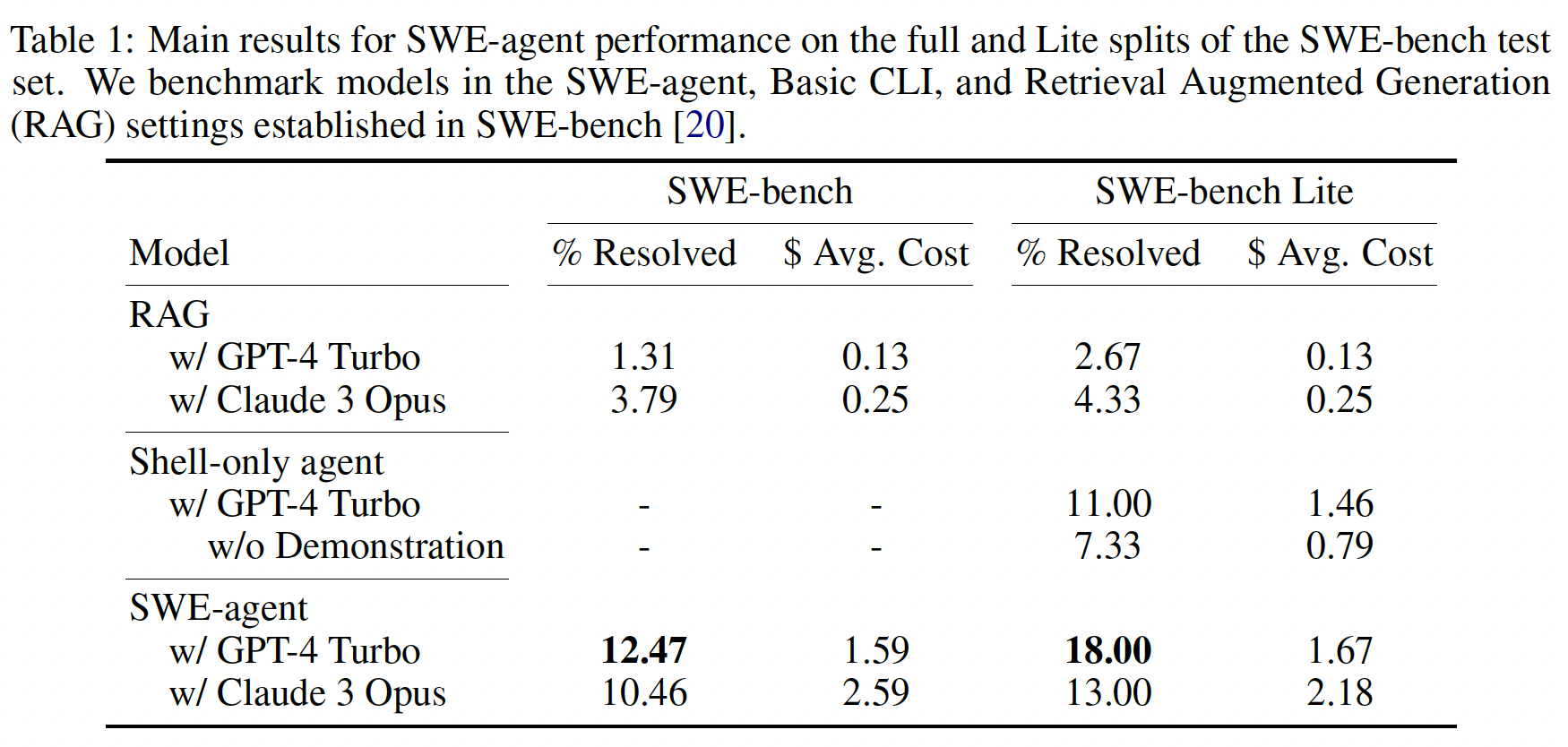
Results#