Linear Regression Variants#
Note
Linear Regression + L2 regularization = Ridge
Linear Regression + L1 regularization = Lasso
Linear Regression + PolynomialFeatures = Polynomial Regression
Ridge#
To lower variance \(\Rightarrow \) limit model’s complexity \(\Rightarrow \) prevent the absolute value of parameters to be large \(\Rightarrow \) we add punishment term concerning the absolute value of parameters on \(J(\theta)\).
Ridge is linear regression plus the \(l_{2}\) regularization term:
\[\underset{w}{\min}\left \|Xw - y \right \|_{2}^{2} + \alpha\left \|w \right \|_{2}^{2}\]
where \(\alpha\) is the regularization hyperparameter.
import numpy as np
n_samples, n_features = 10, 5
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
X = rng.randn(n_samples, n_features)
y = rng.randn(n_samples)
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
clf = Ridge(alpha=1.0)
clf.fit(X, y)
Ridge()
Lasso#
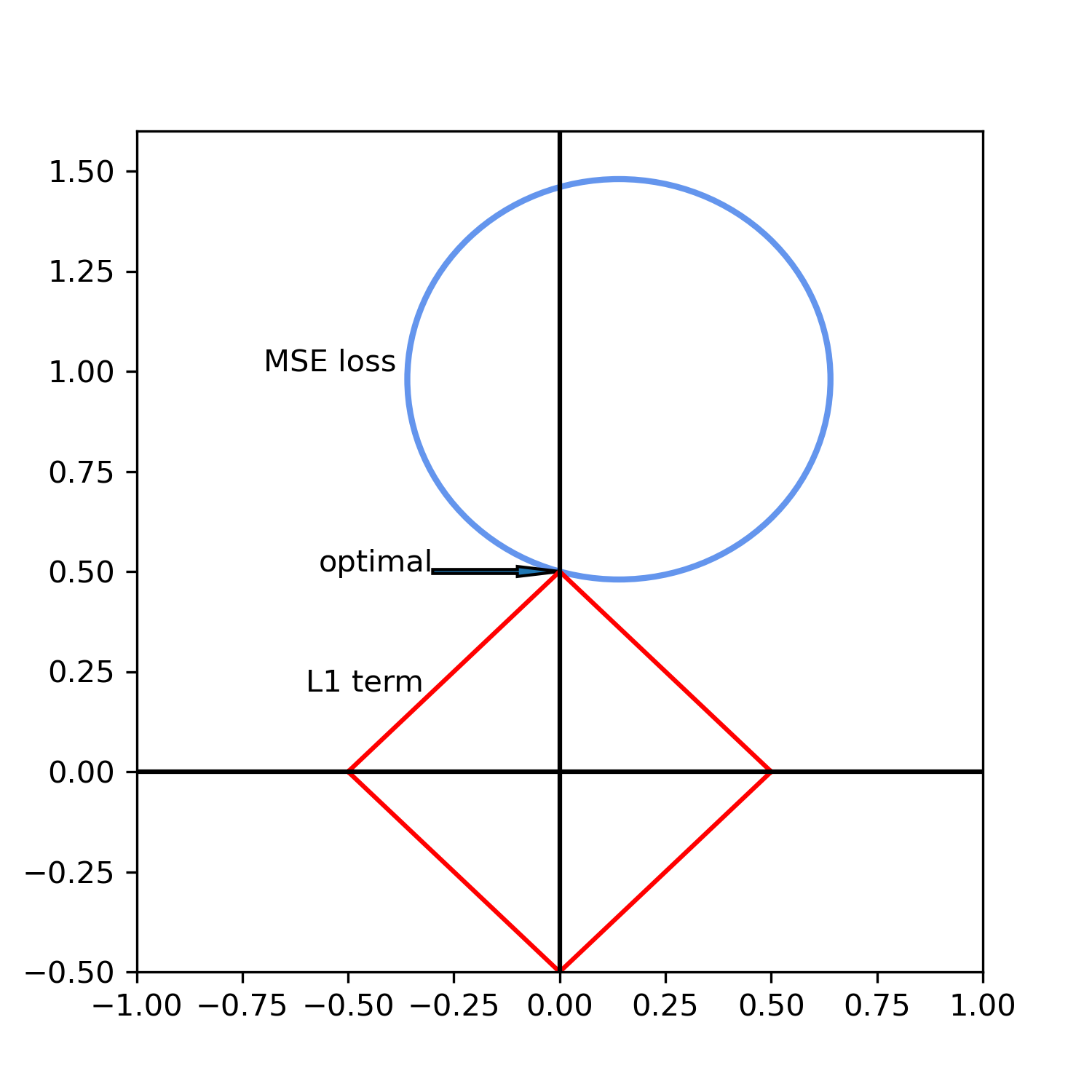
Lasso(Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator) is linear regression plus the \(l_{1}\) regularization term:
\[\underset{w}{\min}\frac{1}{2n_{samples}}\left \|Xw - y \right \|_{2}^{2} + \alpha\left \|w \right \|_{1}\]
Lasso can result in sparse parameters:
from sklearn import linear_model
reg = linear_model.Lasso(alpha=0.1)
reg.fit([[0, 0], [1, 1]], [0, 1])
reg.predict([[1, 1]])
array([0.8])
Polynomial Regression#
"""manual dataset"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
m = 100
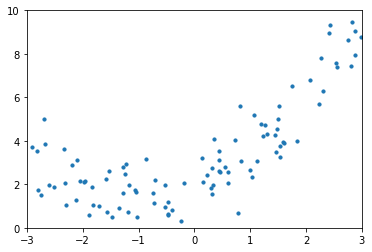
X = 6 * np.random.rand(m, 1) - 3
y = 0.5 * X ** 2 + X + 2 + np.random.randn(m, 1)
plt.scatter(X, y, s=10)
plt.axis([-3, 3, 0, 10])
plt.show()
"""
polynomial regression = PolynomialFeatures + LinearRegression
"""
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
poly_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2, include_bias=False)
X_poly = poly_features.fit_transform(X)
lin_reg = LinearRegression()
lin_reg.fit(X_poly, y)
LinearRegression()
X_new=np.linspace(-3, 3, 100).reshape(100, 1)
X_new_poly = poly_features.transform(X_new)
y_new = lin_reg.predict(X_new_poly)
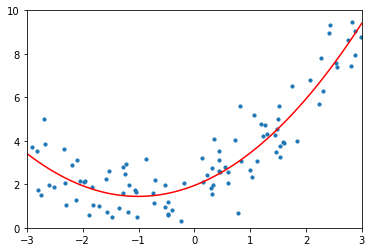
plt.scatter(X, y, s=10)
plt.plot(X_new, y_new, c='r')
plt.axis([-3, 3, 0, 10])
plt.show()